Blockchain-based Application for Privacy and Reliability
This research focuses on using blockchain technology to create smarter and more
efficient systems that benefit society. We developed tools like SCeFSTA
and BARIT, which use blockchain to solve real-world problems. SCeFSTA helps
improve healthcare transportation by making it easier to manage resources,
ensure payments are secure, and allow different providers to compete fairly.
On the other hand, BARIT is designed to make the academic peer review process
better by rewarding reviewers in a secure and anonymous way. Through these
projects, we show how blockchain can be used to create systems that
are not only more secure but also more fair and efficient, helping to build
a smarter and more connected world.
Enhancing Emergency Communication Networks with Edge Computing and UAVs
This research focuses on improving how mobile and emergency communication networks perform,
especially in challenging situations like natural disasters.
One of his key projects, EdgeKeeper, is designed to help first
responders, like firefighters and paramedics, communicate more
effectively when traditional networks are down. Imagine a team
of rescue workers equipped with mobile devices that can form
their own mini-network, allowing them to share information and
coordinate better during emergencies. EdgeKeeper ensures that
this network remains reliable even if some devices stop working
or lose connection. It manages essential tasks like naming devices,
storing important information, and monitoring the network's status,
making sure everything runs smoothly and efficiently.
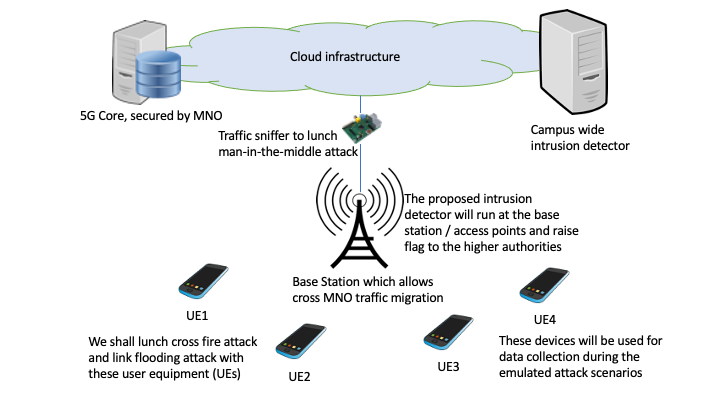
Preserving Privacy and Security in Wireless Networks
The cellular phone system represents the most ubiquitous and trusted communication infrastructure in the world.
The cellular system has evolved a lot in the past two decades, starting from a basic audio communication system
to the current smart phone system. In the last few months, the COVID pandemic has made us realize the cellular network's enormous
importance more, and it has become the most integral part of human life. As the whole nation is looking forward to the jump
from 4G to 5G LTE network, we look for the brighter side of 100x faster download speed, 10x decrease in latency,
and 100x increase in network capacity. However, with all these advantages comes a greater risk of privacy of the users.
The Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Agency (CISA) director Christopher Krebs stated in the August 2020 report
“From my perspective, 5G is the single biggest critical infrastructure build that the globe has seen in the last 25 years and,
coupled with the growth of cloud computing, automation, and future of artificial intelligence, demands focused attention today to secure tomorrow.”
To achieve higher bandwidth and broader coverage, the 5G loosen the network architecture's tight control, which opens several vulnerabilities.
Sustainance against Jamming using Honeynet in Cognitive Radio Network
Open and dynamic spectrum access model brings forth a serious challenge of sustenance among the CRN
and makes them more susceptible to jamming-based denial of service (DoS) attacks. Inspired by
honeypot in the network security, we propose a honeynet based defense mechanism called CR-honeynet.
CR-honeynet aims to avoid attacks on legitimate communications by dedicating a Secondary User (SU) as a honeynode,
to deter the attacker from attacking legitimate SUs and attack the honeynode instead.
Neighbor Discovery for Directional Tranceivers
Directional Radio Frequency (RF) / Free-Space Optical (FSO) transceivers have the potential
to play a significant role in future generation wireless networks. They are advantageous in
terms of improved spectrum utilization, higher data transfer rate, and lower probability of
interception from unwanted sources. Despite these advantages, communications using directional
transceivers require establishment and maintenance of line-of-sight (LOS). Thus, the establishment
of the communication link or neighbor discovery plays a significant role in mobile ad hoc networks
with RF/FSO directional transceivers. In this project, we design protocols for discovering LOS
of a neighbor for both in-band and out-of-band cases.
Mitigate Jamming using Adaptive Beamforming Antenna
In multihop ad hoc networks, a jammer can drastically disrupt the flow of
information by intentionally interfering with links between a subset of nodes.
The impact of such attacks can escalate when the jammer is moving. As a countermeasure for
such attacks, adaptive beam-forming techniques can be employed for spatial filtering of the
jamming signal. This paper investigates the performance of adaptive beam nulling
as a mitigation technique against jamming attacks in multihop ad hoc networks.
Considering a moving jammer, a distributed beam nulling framework is proposed.
Frequency Agile Radio Testbed
Rampant dynamic spectrum allocation over time leads to the creation of narrow
spectrum holes which can be aggregated to fulfill the bandwidth requirements of
users. Even though this approach increases the throughput, it comes at the
cost of degraded spectrum utilization due to a rise in the number of required
guard bands. This project aims at how a transmitter- receiver pair can
coordinate among themselves on choosing the correct frequency and bandwidth
for actual data communication. The next objective is to optimize the spectrum
usage of each transmission such that the nodes can dynamically adapt to the
environment and enhance resource utilization.
3D Obstacle Compliant Mobility Models for UAV networks in ns-3
UAV networks are envisioned to play a crucial role in the future generations
of wireless networks. Due to the high cost of failures in system-based tests,
initial analysis and refinement of designs and algorithms for UAV applications
are performed through rigorous simulations. To facilitate such simulations for
UAV systems, we presents different mobility models for emulation of a UAV's
movement. We further extend these models by considering the effect of large
obstacles on movement patterns following the three models. The mobility models
are prepared as open-source add-ons for ns-3 network simulator.
Enhance Performance of Voice Service for Congested Network
This research focuses on improving Voice over IP (VoIP) performance on
wireless networks, ensuring clearer and more reliable internet voice
calls. One of his significant contributions involves optimizing
Wi-Fi networks for better VoIP quality. He developed a unique method
to adjust network settings, reducing issues like dropped calls and
delays. This was tested using a simulation program, which showed
notable improvements in call quality. Additionally, Dr. Bhunia
studied the performance of WiMAX, a wireless technology that
covers larger areas than Wi-Fi, especially when users are mobile,
such as in cars or trains. He discovered that using adaptive
modulation and coding (AMC) techniques enhances the performance
for high-speed mobile users. His research identified the extended
real-time polling service (ertPS) as the best scheduling service
for VoIP applications due to its balance of delay, jitter, and
packet loss.
Evaluate Performance of WiMAX
In WiMAX deployment, the challenges to service providers lie with the Quality
of Service (QoS) under varying fading environment while at the same time maximizing
for resource utilization. In this research, a rigorous and comprehensive
performance study of mobile WiMAX has been made with respect to
adaptive modulation and coding techniques considering the variation in
the speed of the mobile, path-loss, scheduling services and application
type for comparing with the fixed type of modulations.